Download PDF
Download page Mid-Term Cancellation of Products.
Mid-Term Cancellation of Products
Mid-term cancellation of a product or a service essentially implies canceling the product or service in the middle of the contract term. For example, the annual contract period is from 01 January 2024 to 31 December 2024 for a recurring product with a monthly billing cycle. If you want to cancel it between 2 January 2024 and 31 December 2024, it is a mid-term cancellation. You can do a mid-term cancellation of a one-time, recurring, or evergreen product when the billing periods are either invoiced or not invoiced.
When none of the billing periods are invoiced, it implies that all the Billing Schedule Records (BSRs) and the Billing Schedule Details (BSDs) are still in the Pending Billing status. When you initiate the cancellation process, the cancellation of impacted BSRs and the BSDs is governed by the cancellation date, coinciding with the period start date or falling within the billing period. The cancellation of adjustments, if any, is also governed by the cancellation date. The Status field on the Billing Header (BH) is updated to Pending Inactivation and the Pending Invoice Amount field is updated to USD 0.00 since there is nothing to refund.
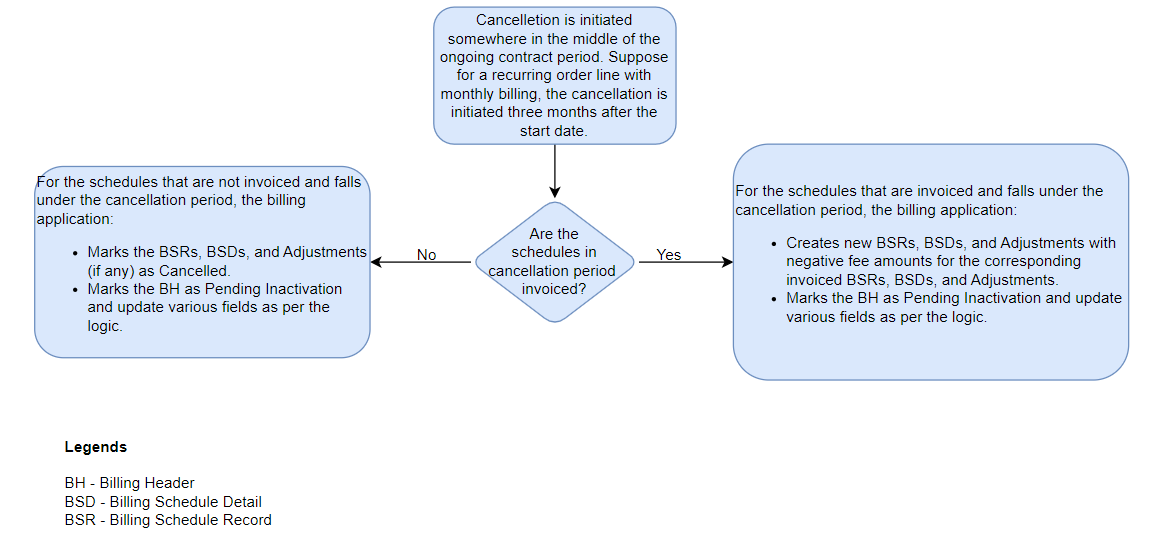
When some billing periods are invoiced, it implies that at least one or few of the BSRs and the corresponding BSDs are in the Invoiced status. When you initiate the cancellation process, new BSRs and BSDs with negative fee amounts are created for the corresponding invoiced BSRs and BSDs falling in the cancellation period. The Status field on the BH is updated to Pending Inactivation, and the Billable Amount from the Current Order Line, Total Invoiced Amount, and Pending Invoice Amount fields are updated as a result of the rolled-up fee amount of the new BSDs. The concept is illustrated in the following diagram:
Suppose the setting is set to "minimize". In that case, the engine limits the superseding of the schedules by creating a billing schedule detail (BSD) with a delta fee under the existing billing schedule record (BSR). if there are any BSRs in pending billing status and they are in the cancellation zone, the engine creates a new counter BSD under that BSR with a negative fee amount equal to that of the existing BSD.
If the setting is set to "always supersede" the engine supersedes the uninvoiced schedules (BSRs) of the impacted period and creates new BSRs and BSDs with the overall fee for that period.
Irrespective of the above settings, the engine's cancellation behavior is not altered, and the calculated amounts in the various fields on the billing header (BH) remain unchanged.
For more on how Billing works on the Conga Platform, see Understanding the Billing Architecture on Conga Platform.
Based on the pricing source chosen in the Billing Settings, the pricing information is fetched from the Order Line Item (OLI) or Asset Line Item (ALI). When the pricing source is set to OLI, Billing fetches all the information, including the pricing information, from the OLI. If the pricing source is set to ALI, Billing fetches the pricing information from the ALI. For more details on pricing sources, see Managing Pricing Source.
For more information on mid-term cancellation of products, refer to the following sections: